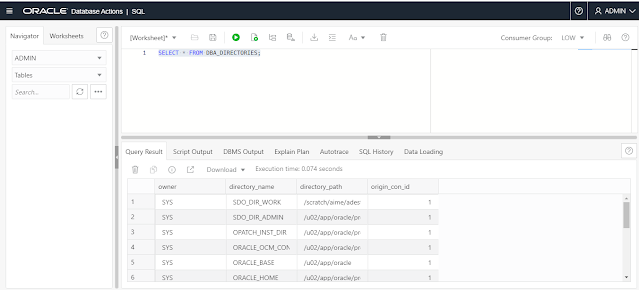
PT - OS TOP commands Monitoring
Top Command Header
Top | users | load average | Tasks | cpu | Memory | swapping
| Field/Section | Meaning |
| load average | This line displays the load averages over the last 1, 5 and 15 minutes. The higher the load average, the more work the machine is doing. A high rise in the load average could indicate a serious performance problem. |
| Tasks | Number of processes that are running, sleeping, stopped, or zombie. In a healthy system, this number does not change a lot by time. |
| Cpu(s) | CPU% usage by user (%us), system (%sy), nice (%ni), idle (%id), I/O wait (%wa), Hard Interrupt (%hi), soft interrupt (%si), and iosteal (%st) which is used in VM environments. Note: in top output, %wa is the only I/O load indicator. |
| Mem | Total physical memory, used memory, and free memory. |
| Swap | Information about swapping. |
| PID | Process Id. Used to know the relationship between the processes and for killing processes |
| USER | The effective user name of the task’s owner. |
| PR | Process priority |
| NI | Process nice value |
| VIRT | Total virtual memory used by the process |
| RES | Non-swapped physical memory used |
| SHR | Shared memory used by the process |
| S | Process status |
| %CPU | Processes percent of CPU consumption since last screen refresh |
| %MEM | Percentage of memory consumption by the process |
| TIME+ | Total CPU time, showing hundredths of seconds |
| COMMAND | Command used to start the process |
| Key | Impact |
| [Shift]+[O] | Sort by a selected field (try sorting by memory, swapped size, command name) |
| [Shift]+[P] | Sort processes as per CPU utilization |
| z | highlight running processes. Press again to disable it. |
| c | Display the absolute path of running processes |
| d | Change screen refresh interval (by default it is 3) |
| k | Kill a process by its PID |
| q | Quit |
- Display order by memory usage